What is a bandwidth limiter?
A bandwidth limiter can be used as a stand-alone method to reduce bandwidth consumption for a particular device. In this section, we’ll briefly discuss how to setup a bandwidth limiter to monitor and control bandwidth.
Just to be clear, Quality of Service is designed to prioritize one type of traffic over another. A Bandwidth Limiter actually caps the bandwidth, regardless of what else is going on within your network. This works entirely independent from any QoS rules you configure (if any).
“It’s just me, my wife, two kids, and a dog. Why should I care about bandwidth?”
If you’ve noticed a significant change in your Internet speed, it might be that a device on your network is hogging the resources. A bandwidth limiter can “level the playing field” and make sure that each computer receives adequate bandwidth. This helps to prevent pages from loading slowly when someone else on the network is downloading music, videos, etc. If you stream videos from NetFlix, Hulu, or Amazon Prime, you most certainly want to setup a bandwidth limiter. This will prevent media from buffering and loading slow during popcorn-hour.
How do I setup a bandwidth limiter?
Assuming that you already have Tomato firmware installed on your router, the first thing to do is locate the computer that is consuming the bandwidth. Let’s do that now . . .
Bandwidth usage can be checked in “real-time” or historically (Daily, Monthly, etc). If the issue is happening this very moment, you can view the IP traffic graph for a real-time view of the TCP/UDP connections, inbound connections, and outbound connections. This can be done from within the Tomato Web GUI. Login to the router.
Navigate to: IP Traffic > View Graphs

Bandwidth Monitor
- Server = 192.168.88.2
- Laptop = 192.168.88.152
It’s not unusual for the server to have more connections than other computers on the network. However, the laptop is supposed to be idling but it appears that it has several connections also. It must be doing something in the background. First, let’s see if this is a one-time event or if it’s been happening over a period of time.
Navigate to: IP Traffic > Monthly

IP Traffic (monthly)
Once you’ve navigated to the IP Traffic menu, click the option to ‘Show known hostnames’. Doing so makes it that much easier to determine which device is using the most bandwidth.

Bandwidth usage (daily)
Once you’ve discovered which device is the culprit, the next step is to determine what application or service is causing the computer to use so much bandwidth. In this case, our laptop was using an above-average amount of bandwidth.
In Windows 7, open the Task Manager by right-clicking your mouse in the bottom toolbar, then select ‘Start Task Manager’

Task Manager
Select the ‘Processes’ tab.
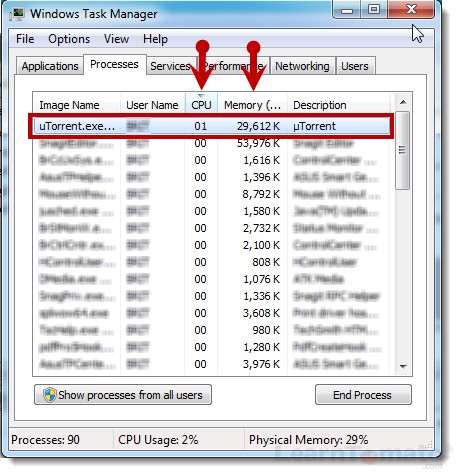
Active Processes
The ‘Processes’ tab displays active applications. It also displays the amount of Memory and CPU resources used by the application. To find the application consuming the most resources, click the column labeled ‘CPU’. Make sure the tiny arrow in the column header is pointed downward to ensure that the filter displays data from greatest to least. Do the same with the ‘Memory’ column.
Be diligent here. Just because an application is using the most resources doesn’t necessarily mean it’s using the most bandwidth. In our case, it was. It was a program called uTorrent. Ever heard of it? 🙂
For those of you unfamiliar with torrent files, its basically a software utility used for downloading shareware, media, and other files. The catch is that when you download, you also become a “seeder” for the file that you’re downloading. This means that others are downloading pieces of the file from your network too. The ideas is that everyone shares the “load” when downloading. The concept is fair enough, but seeding uses a lot of outbound bandwidth.
Instead of ending the program entirely, we’ll simply limit the amount of bandwidth to and from the laptop using the Bandwidth Limiter within Tomato.
Launch the Bandwidth Limiter
Navigate to Status > Device List

Device List
Make sure the computer you wish to limit is turned on so that it shows up in the device list. Locate the device and click the tiny link named ‘bwlimit’ just below the device name. Doing so will load the device information into the Bandwidth Limiter. The next screen has a few options. Let’s break this page down to make it easier to understand.
Enable the Bandwidth Limiter

Enable Limiter
Enable the Bandwidth Limiter and enter the max upload and max download in Kbps (Just like we did in the last chapter for QoS rules).
Configure the Upload and Download Rates

Download Rates and Ceilings
You have a few options here. You can enter:
- The IP address
- A Range of IP addresses
- The computers MAC address
If you enter the IP address, be sure that machine has a static IP. Why would you want to enter a range of IP addresses? Suppose these devices do not have static IP addresses. Suppose they receive dynamic IP’s. The next time your laptop connects to the network and receives a new IP address, the bandwidth limiter will fail to work. However, if you enter the physical MAC address of the computer, it will not matter what the IP address is.
What is the DL Rate?
The download rate is the minimum download capacity when other machines on the list are also downloading. This way, the router can ensure that the device receives at least this much bandwidth while other computers are downloading as well. Essentially, you want to plan your entries because the total DLRate cannot exceed the maximum available download limit. For example, if you have a max bandwidth download of 40,000Kbps, and you have 4 computers, you might set each computer to have a max DL rate of 10,000Kbps.
What is the DL Ceiling?
The Download Ceiling is the available download bandwidth when other computers are not using the bandwidth allotted to them. If they are not using their bandwidth, one machine can take advantage of more bandwidth.
Upload Rate and Upload Ceiling work the same as for downloading.
Set Priority and TCP/UDP Limits

Priorities
Priority – The higher the priority, the more preferential treatment the computer or device will receive. Primarily this affects DNS traffic such as browsing and gaming.
TCP Limit is the maximum number of connections allowed for this IP, IP range, or MAC address, and any given time. This is helpful in controlling download utilities and torrent programs such as described above. In such case, only 20 active TCP connections would be allowed.
UDP Limit is the maximum number of connections allowed for UDP traffic. Remember, UDP protocol is used mostly for one way communication such as video streaming. For example, this computer would only be able to stream to 5 other devices.
